Last updated: 2025-04-16
Validating MongoDB Documents in Spring Boot
MongoDB now available in the Free plan! Create your next Spring Boot app with custom database schema in minutes - following best practices and providing validation for MongoDB.
Discover more
There are two ways to validate documents stored in a Spring Boot application using MongoDB. After describing the basic structure of such an application in a previous article, this article will focus on the specific question of validation.
MongoDB allows to persist any collection with any data structure at any time. However, for an application that is intended to be in productive use for a long time and where other applications may also access the database, an explicitly defined database schema is an advantage. This way, a developer knows what to expect, and programming is simplified.
Validation via constraints
One way is to add field validations from the jakarta.validation package directly to the documents contained in our application. To activate those constraints, we first need to include a dependency, which is not present in Spring Boot by default:
We also need to extend our configuration class so that our persistence layer actually performs the validations.
Providing the ValidatingMongoEventListener as a bean
Now we can use the well-known annotations to ensure the validity of our fields. In the following document a few examples are listed, e.g. @NotNull (required field) or @Size (length of the string). These will now be checked before saving.
Adding constraints to our Address document
Validation via JSON schema
MongoDB offers the possibility to specify an explicit JSON schema for a collection. This checks the restrictions defined there for all saved documents - so these also apply to other applications that want to store data in the database. In our example we check the required fields as well as the data type.
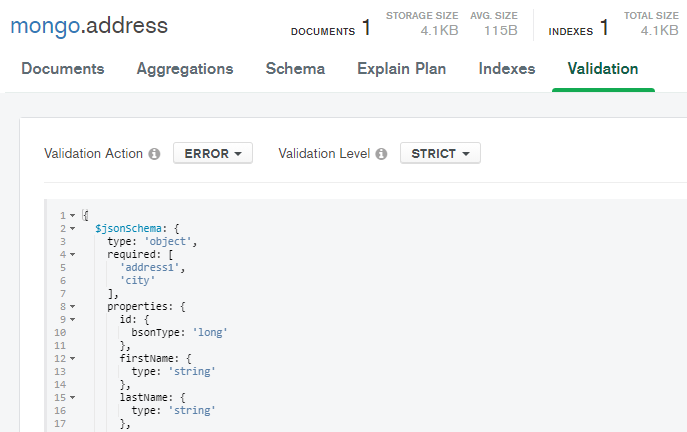
A MongoDB collection with a basic JSON schema
To create such a schema, it is a good idea to use a ChangeLog executed by Mongock. This initializes the collection with the defined schema when our application is started. Since creating collections within transactions is not possible, we use the @BeforeExecution hook at this point. The next article will explain how to setup Mongock.
Changelog to initialize our address collection with additional options
In the Free plan of Bootify, Spring Boot apps can be configured with a custom database schema. When MongoDB is selected as the database, the documents are generated along with their constraints. In the Professional plan, Mongock is available as an option to additionally initialize the collections with a basic JSON schema.
Further readings
MongoDB schema validation
jakarta.validation constraints