Last updated: 2024-07-04
Persisting JSON with Spring Data
The Bootify Builder automatically prepares the setup and annotates your custom entities with the proper JSON type - suitable for your selected database. Available in the Free plan without registration.
Discover more
Basically every modern database system has its own data type to persist JSON. Using this type ensures correct formatting of the input, as well as other advantages such as faster I/O. How can we add JSON fields to our entities in Bootify?
With Hibernate 6 we can directly map our JSON fields using Hibernates @JdbcTypeCode(SqlTypes.JSON) annotation at our entities. The technical backgrounds are explained in this article.
We begin by clicking start project - no registration required. Then we go to the Data Objects tab and first create the object "PartDetailsDimensions" with its three fields.
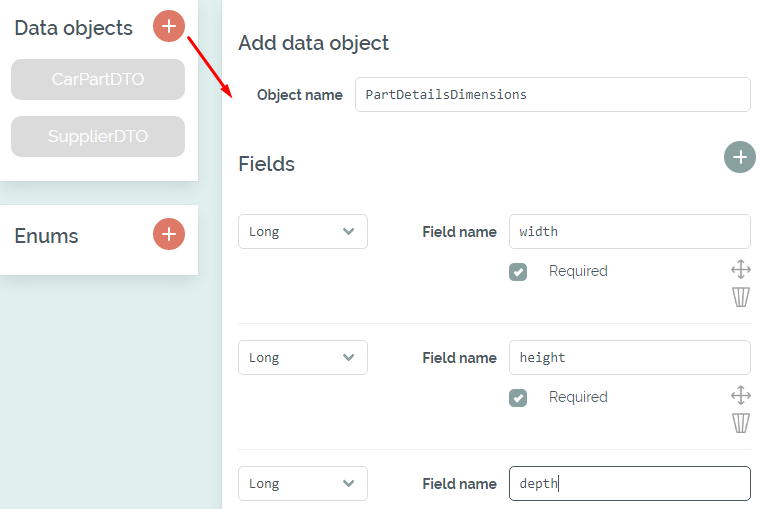
Adding the PartDetailsDimensions data object
Now we create the object "PartDetails". Since "PartDetailsDimensions" already exists, we can select it directly as a custom type.
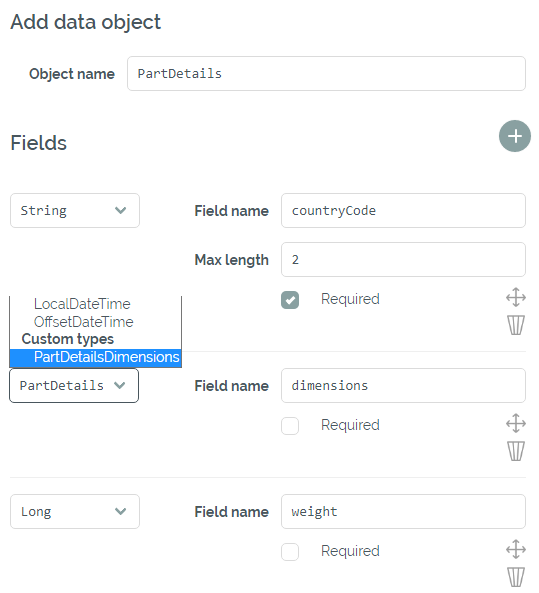
Adding the PartDetails
Finally we can switch back to the Entities tab and create the CarPart entity if doesn't already exists. Here we can now add the field "partDetails" with its corresponding type PartDetails.
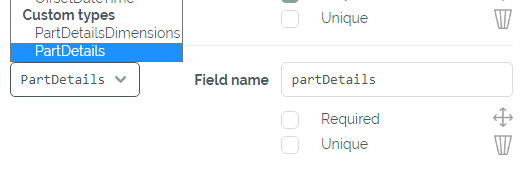
Adding the new field to our entity
That's it! Depending on the database a certain type and column definition is necessary - this is automatically provided by Bootify together with all the setup around it. Our data objects can also be used for a custom REST API or custom frontend controller.
Start Project
No registration required